#UpExperts | Edition 6 is live! See how to choose the right Salesforce Integration Patterns for different projects.
#UpExperts | Edition 6 is live! See how to choose the right Salesforce Integration Patterns for different projects.
In our previous article, we explored key architectural patterns and when to use them. Now, together with Ivy Li, our Salesforce Senior Developer, we shift focus from what the patterns are to how they’re applied in a real-life Salesforce integration project. Let’s dive into our use cases!
The Integration Landscape:
A Salesforce Consultant has been involved in a project to support a Trendy Play client’s Salesforce Storefront with their integration.
There are more than 200 internal sales users and 5,000+ registered customer users in the system. Large amount of data transfers among the systems every day, to provide good user experience is very important, so high-quality integration is the top priority for support.
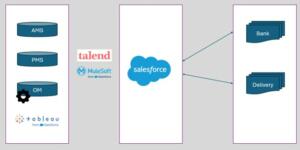
The company has internal systems for different business purposes:
Salesforce Customer Portal: Sales center, customer can follow the new released products, place order, track order static information
Account Management Database (AMD): Local Database for Customers and shipping addresses, Users’ information with their relationship with the Customers
Product Management Database (PMD): Product Catalogs, Product Storage, Pricing
Order Management (OM): Orders, Order History
The company also has integrations with external systems:
Bank: Credit validation and Payment
Delivery: Statics system
The Consultant reviewed the integrations and analyzed the patterns for some use cases:
Case #1: Customers and Users information should be aligned between AMD and Salesforce Storefront.
Analysis: Customers’ and Users’ data do not change frequently; the bi-side integration is a daily based batch loading with a serious number of jobs. Several jobs run in sequence once every mid-night, during the period when there are not too many customers visiting the website.
Patterns: Batch Data Synchronization
Solution: Talend
Talend provide monitoring tools to manage jobs, track the job status, performance and errors for trouble shooting any errors.

Case #2: Product, Product Storage and Product Pricing should be aligned between PMD and Salesforce Storefront every 15 minutes.
Analysis: PMD is the system of truth. New products may be released in the daytime to make sure customers can order the products at first time when they released.
Patterns: Remote Call-In and Batch Data Synchronization
Solution: Talend
Talend provides rapid data integration, transformation, and mapping with automated quality checks to ensure trustworthy data every step of the way.

Case #3: Before submitting an order, the customer needs to review the order summary, including the shipping address, detailed product list, price, tax, and courier charges from the Delivery system.
Analyze: When customers move to the order summary page, Salesforce Storefront need to share Delivery system some information like the shipping address, the package weight and size so that Delivery system can estimate the courier charges, plus the product price and tax, generate an order summary for customer review.
Patterns: Event-Driven, Remote Request/Reply
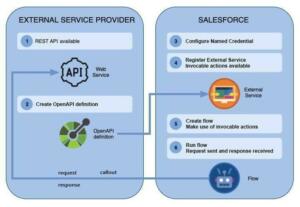
Solution: Salesforce Flow with External Services
Salesforce Flow with External Service provides low code/ no-code integration between Salesforce and external systems through APIs.
Case #4: Before submitting the order, Salesforce storefront should check whether the user has enough Bank credit to proceed with the payment.
Analyze: On the order review page, the customer clicks the “Check-Out” button and waits for several seconds. When they confirm the payment result, the order review page is refreshed and shows successful information.
Patterns: Event-Driven, Remote Request/Reply, UI Update on Change
Solution: Apex Callouts
Apex Callouts provides customized callout based on RESTful API or SOAP API; analyze the response and reflect on Salesforce Database or UI in real time.
Case #5: When the order submitted, the order detail information should push from Salesforce storefront to PMS, OM, external Bank system and external Delivery system.
Analyze: Many validations are finished when the customer submits the order. Order submission will change the order status in Salesforce, then notify other system to proceed their process, for example: notify the PMS to deduct the storage, notify the OM to track the order, externally, notify the Bank system to proceed the payment and Delivery system to start the delivery.
Solution: Change Data Capture (CDC), MuleSoft
Patterns: Event-Driven, Remote Fire and Forget
Change Data Capture will capture the record change and publish them as events in near real-time. MuleSoft is a middleware that subscribes to events and flows to different other systems.
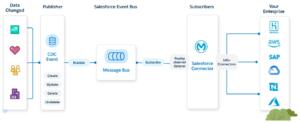
Case #6: Customers can review order history for more than 5 years from OMS and are able to track the courier information from the external Delivery system for all orders.
Analyze: Order detail information archived to OMS periodically to release Salesforce storage and improve user experience, when user reviewing the order history, the information was getting from OMS and display on Salesforce storefront, no local data need to be saved.
Patterns: Data Virtualization
Solution: Salesforce Connect
Salesforce Connect provides integration from external data sources without importing the data into the salesforce object. It is a real-time, on-demand connection to access and display external data as if it were native Salesforce records.
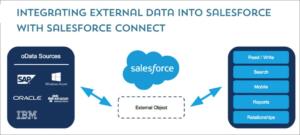
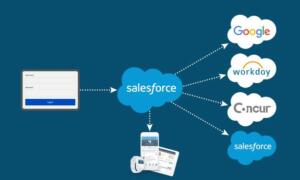
Case #7: Storefront is available for customers to log in with Google, Facebook, Microsoft, LinkedIn, or register with their mailbox.
Analyze: Users can easily login with their existing accounts; authentication is handled automatically from background to background with Salesforce configuration only. If the user wants to register a new account, the registration will take 1-2 minutes with the standard experience cloud registration feature.
Patterns: Event-Driven, Remote Call-In, UI Update on Change
Solution: Single Sign-On (SSO), Authentication Providers
Single Sign-On (SSO) and Authentication Providers allow users to log in using accounts from other platforms with configuration only.
Case #8: Dashboard about sales, customers and products
Analyze: Directors can easily know the best-selling products, best-purchased customers and summary of sales users, sales teams, by customers, by products in different dimensions.
Patterns: IFrame, Interactive Embedding Pattern, Single Sign-On (SSO)
Solution: Tableau
Tableau is a Salesforce Business Intelligence (BI) product to provide data visualization. It helps users understand and analyze data through interactive, visual dashboards with deep and stable integration with Salesforce environments.
Do you want more insights?
This article shows how integration patterns aren’t just theory — they’re key to building resilient, scalable, and user-focused Salesforce systems.
Missed the previous one?
Check out: Salesforce Design Patterns every developer should know
Curious about the reasoning behind each pattern choice?
Let us know — we’ll gladly go deeper into the decision-making process in a future edition.